Exploring the Merits of 3D Printing vs Traditional CNC Manufacturing
Today, we aim to explore the advantages and disadvantages of both 3D printing and conventional CNC fabrication in prototype development.
A prototype is a physical model or sample produced prior to the commencement of mass production without undergoing moulding process. It serves as an initial step towards product feasibility validation and a direct yet effective method for identifying defects, deficiencies, and shortcomings within the design to facilitate targeted refinement. This practice aids designers in optimizing the design plan, curtailing subsequent production costs, and hastening product launch timeframes. Thus, prototyping plays a crucial role in product research and design advancements.
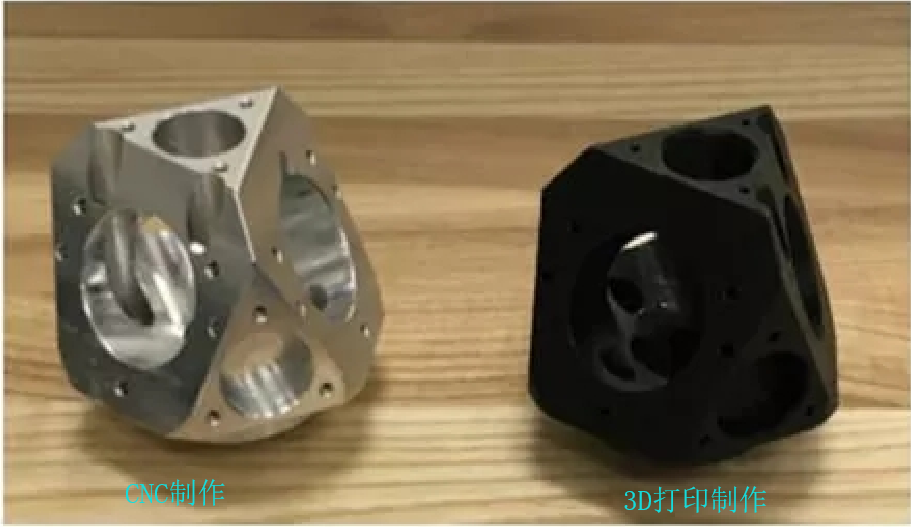
Advantages of 3D printed prototypes:
(1) High material utilization;
(2) Swift forming speed;
(3) Capability to machine intricate structures inconceivable by CNC;
(4) Exceptional precision;
(5) Straightforward operation;
(6) One-time formation.
Perks of CNC manufactured prototypes:
(1) Mature craftsmanship leading to cost control across large-volume productions;
(2) Robust size;
(3) Precision capability;
(4) Superior surface quality;
(5) Robustness and flexibility are paramount.
Disadvantages of 3D printed prototypes:
(1) Desktop 3D printers possess average surface quality, strength, and toughness, with limited capacity;
(2) Industrial-grade 3D printers prove expensive for high-quantity procurement.
Turning to CNC fabricated prototypes:
(1) Lower material efficiency;
(2) Complex structures necessitate multiple machining steps beyond feasibility;
(3) Operators require advanced skills.
As an extensively utilized rapid prototyping technology in manufacturing sectors, 3D printing finds application primarily in prototype developing. Comparative discussions on this realm have invariably showcased the prowess of both 3D printing and traditional CNC prototyping techniques. As an additive manufacturing technique, 3D printing primarily functions by accumulating materials to fabricate required object forms. Therefore, ongoing material addition is integral in the production cycle, making it known also as layer-by-layer construction. Conventional CNC prototyping, conversely, employs subtractive manufacturing methods that involve material excision to shape the final product. Consequently, a single complete material cut is required throughout the production phase for ultimate end result attainment. Despite these variations in products’ creation processes, they serve effectively in prototype manufacture, each offering distinct advantages. Thus, amalgamating them into a comprehensive prototyping strategy can be highly beneficial. In case complex product structures with stringent product accuracy requirements need to be created, 3D printing emerges as a toppick. Owing to its proficiency in crafting intricate structures and attaining higher precision levels, 3D printing emerges as a top pick. Conversely, if relatively simple structures with relaxed accuracy standards are required for production, then conventional CNC prototyping meets the needs of production due to its superior processing precision.
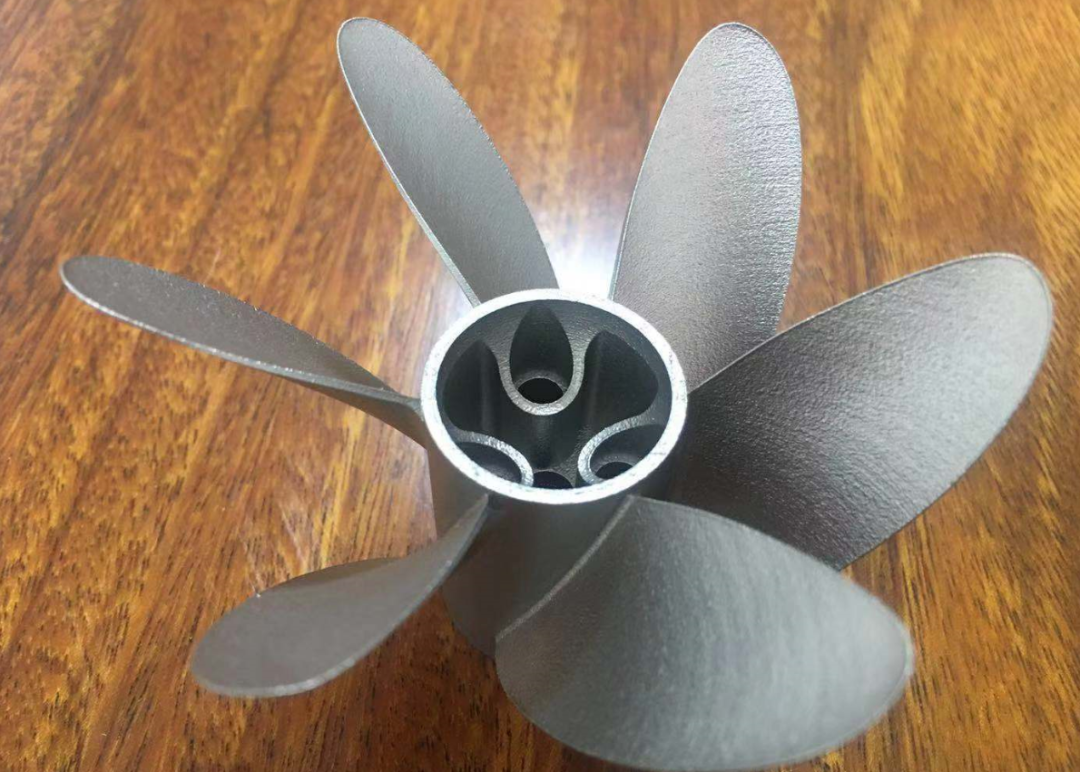

If you do have any questions, kindly feel free to explore our official website or kindly reach out to me directly for elucidation.
Website Address: www.brozan3dprinter.com
Whatsapp: +86 15716101282
